Machine Tool Calibration for Accurate Results
Precision industries require high accuracy component manufacturing. To make these high value parts, not only does a CNC machine need to be repeatable but it also needs to be accurate. To help customers obtain accuracy, Polaris UniverseOne™ motion control systems come equipped with a number of compensation, calibration and distortion correction features for CNC machines and galvo scan heads.
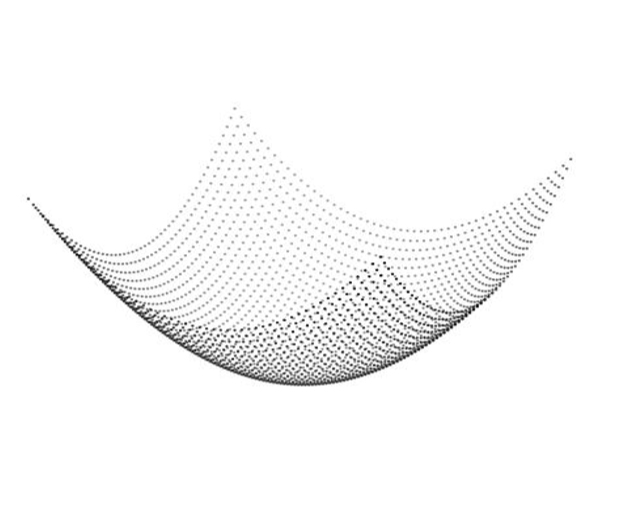
Field Flattening for 2D and 3D Galvoscanners
When a Galvoscanner uses two deflection mirrors, one for X motion and another for Y motion, and a moving front focusing lens, the focusing surface is in the shape of a bowl for each position of the lens.
However, a flat focal plane is desired in most manufacturing processes. A Polaris UniverseOne™ accomplishes this with a motion controller that provides a field flattening function. An algorithm executes movement of the lens so the focusing distance of the laser spot creates a focus plane as X and Y are traversed.
This function may be employed for a 2D Galvo scan head to keep focus over a flat surface if a f-theta lens is not being used. More commonly, this approach is used with 3D Galvo scanners, for the ability to focus on flat planes of arbitrary height.
Backlash Compensation
Transmission systems which use gears and screws often have some amount of direction dependent backlash. This is easily compensated using standard Polaris UniverseOne™ compensation function.
1D Encoder Compensation
Precision actuators or encoders often ship with laser calibrated compensation tables. The axis is easily made more accurate by applying Polaris Motion’s 1D compensation function.
2D Encoder Compensation
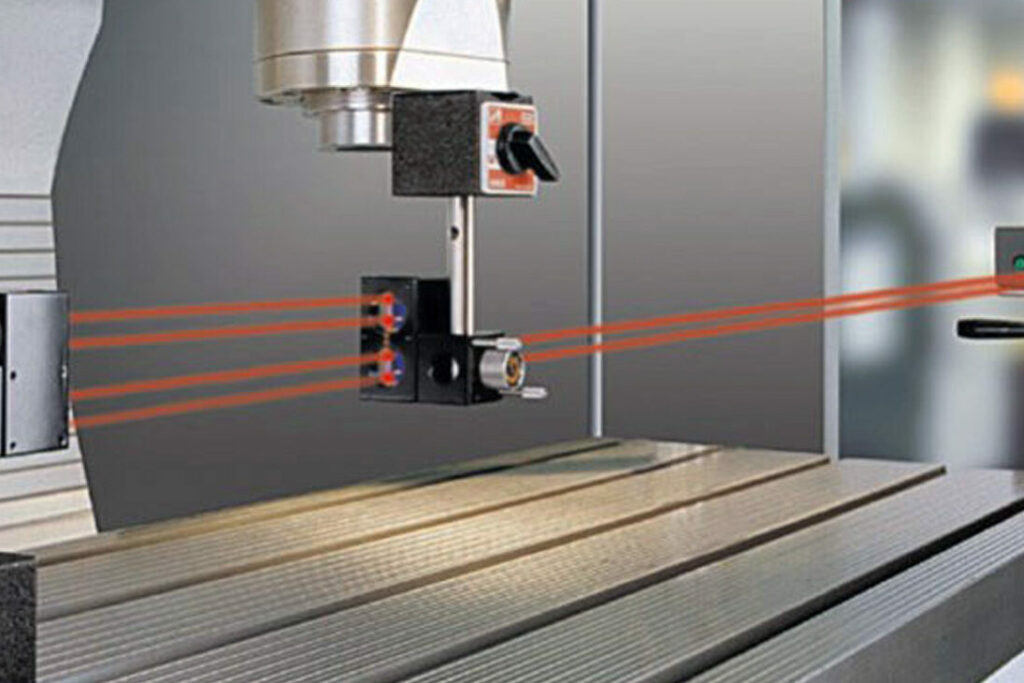
Two and three-dimensional Cartesian stages (XY and XYZ) may be purchased according a variety of accuracy grades. The stage manufacturer may perform a laser calibration service at their factory and supply the calibration tables along with the stage.
Alternately, the machine may be calibrated using a laser tracker or multi-axis calibrator on site. Polaris UniverseOne software is full featured and provides for linear, horizontal straightness, vertical straightness, roll, pitch, yaw and height map compensation.
2D Lens Calibration
Optical distortion is inherent in pre-calibrated laser Galvoscanners systems. Each laser galvo scan head needs to be calibrated to correct the barrel-pincushion distortion.
A Polaris UniverseOne™ motion control system offers an advanced, curves-based laser optic calibration process. This unique process preserves the smoothness and continuity of higher order derivatives for superior overall Galvoscanner motion quality.
3D Lens Calibration
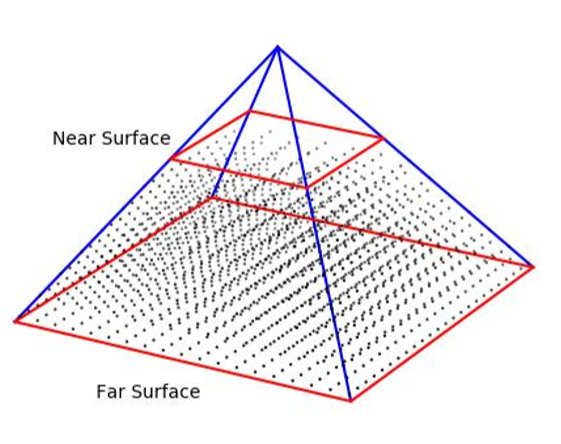
For 3D galvo scan heads, in addition to X and Y travel, the Z focusing axis is a consideration. The focused laser spot is free to move anywhere inside of its working volume.
Calibration of the 3D system is performed over a number of steps. In the first step, the field flattening procedure is conducted for a number of heights. At each height a grid of fiducial marks is created and measured. The measured data along with the desired field for each of the heights is fed to the off-line calibration algorithm which generates the real-time correction matrix.
The real-time correction matrix is used for producing an accurate working field for the 3D laser Galvoscanner.
